Solar Eclipse Prime Page
Partial Solar Eclipse of 2438 Jan 26
Fred Espenak
Introduction
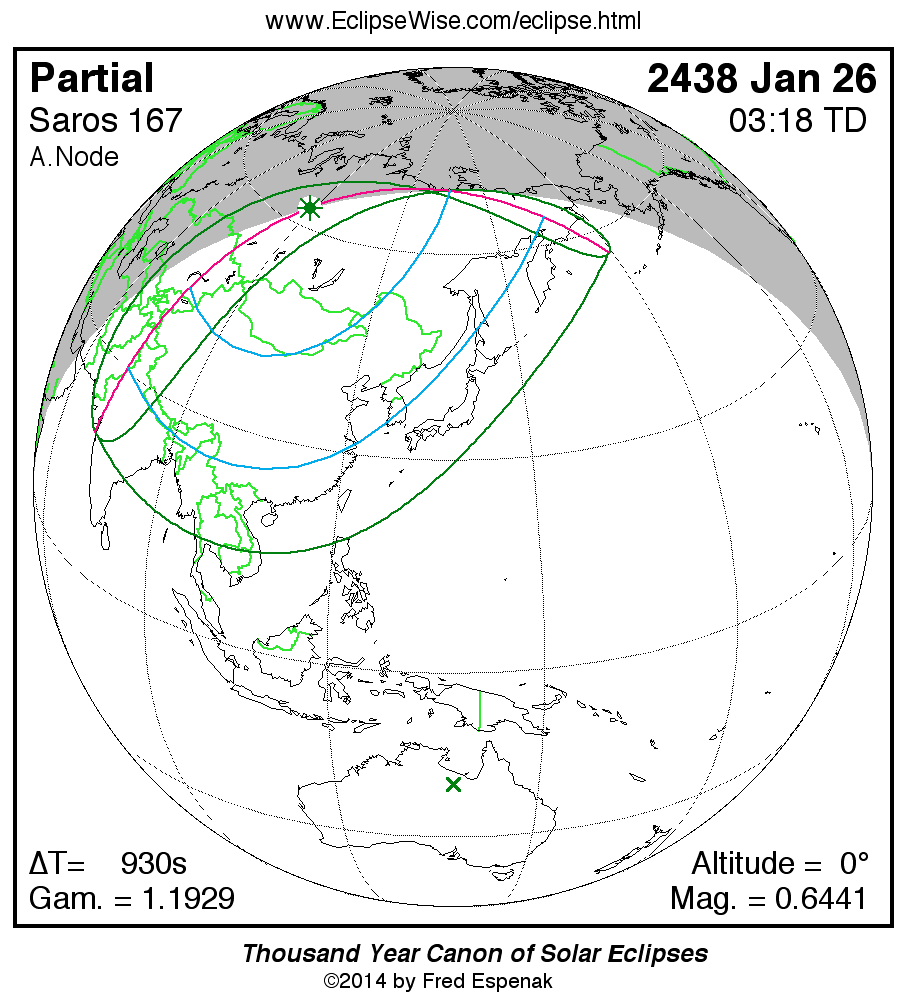
The
Partial Solar Eclipse of 2438 Jan 26
is visible from the geographic regions shown on the map to the right.
Click on the map to enlarge it.
For an explanation of the features appearing in the map,
see Key to Solar Eclipse Maps.
The instant of greatest eclipse takes place on 2438 Jan 26 at 03:17:36 TD (03:02:06 UT1).
This is 1.4 days after the Moon reaches perigee.
During the eclipse, the Sun is in the constellation Capricornus.
The synodic month in which the eclipse takes place has a Brown Lunation Number of 6371.
The eclipse belongs to Saros 167 and is number 14 of 72 eclipses in the series.
All eclipses in this series occur at the Moon’s ascending node.
The Moon moves southward with respect to the node with each succeeding eclipse in the series and gamma decreases.
This is a very deep partial eclipse.
It has an eclipse magnitude of 0.6441,
while Gamma has a value of 1.1929.
The partial solar eclipse of 2438 Jan 26 is preceded two weeks earlier by a total lunar eclipse on 2438 Jan 11.
Another solar eclipse occurs one synodic month before the 2438 Jan 26 eclipse. It is the partial solar eclipse of 2437 Dec 27.
These eclipses all take place during a single eclipse season.
The eclipse predictions are given in both Terrestrial Dynamical Time (TD)
and Universal Time (UT1).
The parameter ΔT is used to convert between these two times (i.e., UT1 = TD - ΔT).
ΔT has a value of
929.7
seconds for this eclipse.
The uncertainty in ΔT is
238.9 seconds corresponding to a standard error in longitude of the eclipse path of ± 1.00°.
The following links provide maps and data for the eclipse.
The tables below contain detailed predictions and additional information on the
Partial Solar Eclipse of 2438 Jan 26
.
Polynomial Besselian Elements: Partial Solar Eclipse of 2438 Jan 26
| Polynomial Besselian Elements |
| 2438 Jan 26 at 03:00:00.0 TD (=t0) |
| n |
x |
y |
d |
l1 |
l2 |
μ |
| 0 | -0.56378 | 1.06466 | -18.6931 | 0.54193 | -0.00421 | 222.1306 |
| 1 | 0.53981 | 0.19503 | 0.0100 | 0.00008 | 0.00008 | 14.9991 |
| 2 | -0.00003 | 0.00006 | 0.0000 | -0.00001 | -0.00001 | 0.0000 |
| 3 | -0.00001 | -0.00000 | - | - | - | - |
| Tan ƒ1 | 0.0047511 |
| Tan ƒ2 | 0.0047274 |
At time t1 (decimal hours), each besselian element is evaluated by:
x = x0 + x1*t + x2*t2 + x3*t3 (or x = Σ [xn*tn]; n = 0 to 3)
where: t = t1 - t0 (decimal hours) and t0 = 3.000
Explanation of Polynomial Besselian Elements
Calendar
The Gregorian calendar (also called the Western calendar) is internationally the most widely used civil calendar.
It is named for Pope Gregory XIII, who introduced it in 1582.
On this website, the Gregorian calendar is used for all calendar dates from 1582 Oct 15 onwards.
Before that date, the Julian calendar is used.
For more information on this topic, see Calendar Dates.
The Julian calendar does not include the year 0.
Thus the year 1 BCE is followed by the year 1 CE (See: BCE/CE Dating Conventions).
This is awkward for arithmetic calculations.
Years in this catalog are numbered astronomically and include the year 0.
Historians should note there is a difference of one year between astronomical dates and BCE dates.
Thus, the astronomical year 0 corresponds to 1 BCE, and astronomical year -1 corresponds to 2 BCE, etc..
Eclipse Predictions
Predictions for the
Partial Solar Eclipse of 2438 Jan 26
were generated using the
JPL DE406
solar and lunar ephemerides.
The lunar coordinates were calculated with respect to the Moon's Center of Mass.
The predictions are given in both Terrestrial Dynamical Time (TD)
and Universal Time (UT1).
The parameter ΔT is used to convert between these two times (i.e., UT1 = TD - ΔT).
ΔT has a value of
929.7
seconds for this eclipse.
The uncertainty in ΔT is
238.9 seconds corresponding to a standard error in longitude of the eclipse path of ± 1.00°.
Acknowledgments
Some of the content on this website is based on the book Thousand Year Canon of Solar Eclipses 1501 to 2500.
All eclipse calculations are by Fred Espenak, and he assumes full responsibility for their accuracy.
Permission is granted to reproduce eclipse data when accompanied by a link to this page and an acknowledgment:
"Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, www.EclipseWise.com"
The use of diagrams and maps is permitted provided that they are NOT altered (except for re-sizing) and the embedded credit line is NOT removed or covered.

